A proper assessment of an organization’s security posture must be performed at the network level and at the OS and application level. Below are some sample questions that are asked and evaluated with a risk profile based from ALE (annual loss expectancy), or consequences as it relates to a (EF) exposure factor with Risk/Breach.

A countermeasure is a security control that is strategically designed to eliminate a vulnerability or at least reduce the likelihood of a vulnerability being exploited. The value of implementing countermeasures is the mitigation of potential risks. The costs of countermeasures involve more than just monetary allocations. There are several areas that need to be assessed and evaluated regarding countermeasure implementations, such as:
- Product costs
- Design/planning costs
- Implementation costs
- Environment modifications
- Compatibility with other countermeasures
- Maintenance requirements
- Testing requirements
- Repair, replacement, or update costs
- Operating and support costs
- Effects on productivity
- Subscription costs
- Testing requirements
We start with assessment for device management and inventory system based on:
- Network Level Security
- Cloud-based
- Hosted-Based and OS
- Application layer
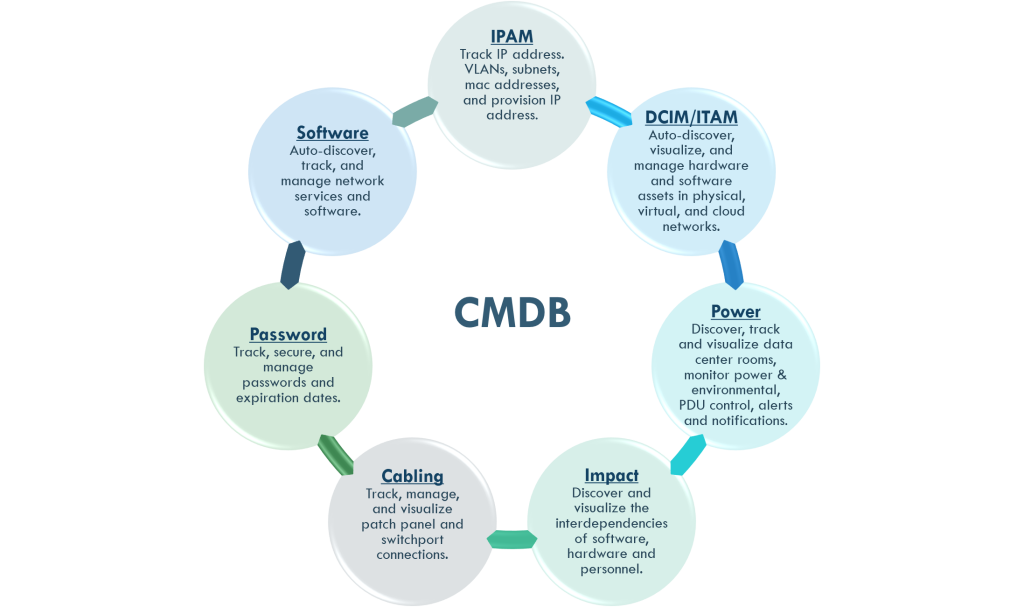
Configuration Management Database (CMDB)
A Configuration Management Database (CMDB) is a repository that acts as a data warehouse for Information Technology (IT) installations. It holds data mapped to a collection of IT assets commonly referred to as Configuration Items (CI), as well as to descriptive relationships between the assets.
CIS Critical Security Controls (CIS Controls)
The CIS Critical Security Controls (CIS Controls) are a concise, prioritized set of cyber practices created to stop today’s most pervasive and dangerous cyber attacks. The CIS Controls are developed, refined, and validated by a community of leading experts from around the world. Organizations that apply just the first five CIS Controls can reduce their risk of cyberattack by around 85 percent. Implementing all 20 CIS Controls increases the risk reduction to around 94 percent.
The CIS Controls embrace the Pareto 80/20 Principle, the idea that taking just a small portion of all the security actions you could possibly take, yields a very large percentage of the benefit of taking all those possible actions:
- Inventory of Authorized and Unauthorized Software.
- Secure Configurations for Hardware and Software on Mobile Devices, Laptops, Workstations and Servers, like OS Harding Images and shell scripts with automation system configuration management tools.
- Continuous Vulnerability Assessment and Remediation.
- Controlled Use of Administrative Privileges.


